concrete
-

Admixture to neutralize Alkali Silica Reaction (ASR) in Concrete
By
Alkali-silica reaction (ASR) is a major durability concern in concrete structures, leading to expansion, cracking, and loss of strength. To mitigate ASR, various chemical admixtures and supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs) are used to neutralize or suppress the reaction. This section discusses the most effective admixtures, their mechanisms, and their application in concrete mix design. Lithium-Based…
-

Delayed ettringite formation in concrete
By
in EngineeringDelayed ettringite formation (DEF) is a chemical reaction that occurs in hardened concrete, leading to internal expansion and cracking. This phenomenon typically arises due to the late formation of ettringite (a calcium sulfoaluminate hydrate) after the concrete has already set and hardened. DEF is a significant durability concern, particularly in heat-cured concrete structures, as it…
-

Testing ASR in concrete before and after construction
By
Alkali-silica reaction (ASR) is a deleterious chemical reaction that occurs between the alkaline pore solution in concrete and reactive silica present in certain aggregates. This reaction forms an expansive gel that can induce cracking, reduce durability, and compromise structural integrity (Thomas, 2011). Given its long-term implications, ASR is a critical concern in concrete design and…
-

Erosion of concrete by wind and water
By
Erosion by water The erosion of concrete caused by hard suspended particles in flowing water presents a significant challenge in the design and maintenance of hydraulic infrastructure. This degradation mechanism is particularly critical for structures such as spillways, stilling basins, and dam outlets, where high-velocity flows and sediment-laden water are common. Erosive processes are primarily…
-
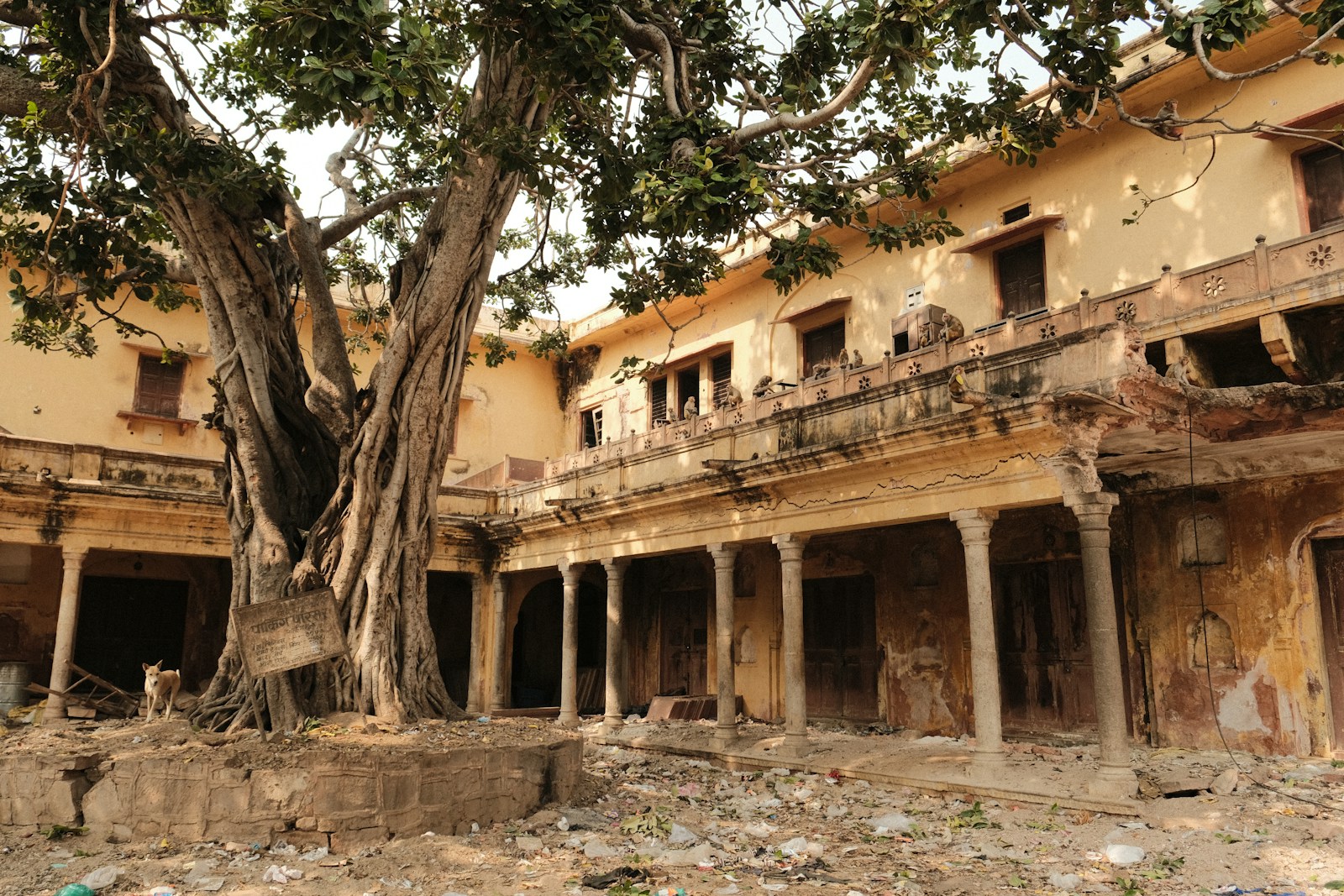

Safety of deteriorated structures
By
The collapse of various civil engineering structures-such as bridges, dams, and buildings-has become a common occurrence in recent years, often attributed to aging and material degradation (refer to relevant news reports). Many of these structures were constructed decades ago, with assumed service lives typically ranging from 50 to 80 years. For instance, the design life…
-
Use of genetic algorithm for optimum proportioning of concrete
By
Genetic Algorithms (GAs) have emerged as a robust optimization technique within civil engineering, particularly in the design of concrete mix proportions. Their inherent ability to address complex, multi-objective, and nonlinear optimization problems makes them well-suited for this application. Conventional mix design methodologies often rely on iterative, trial-and-error approaches that are both time-consuming and may fail…
-
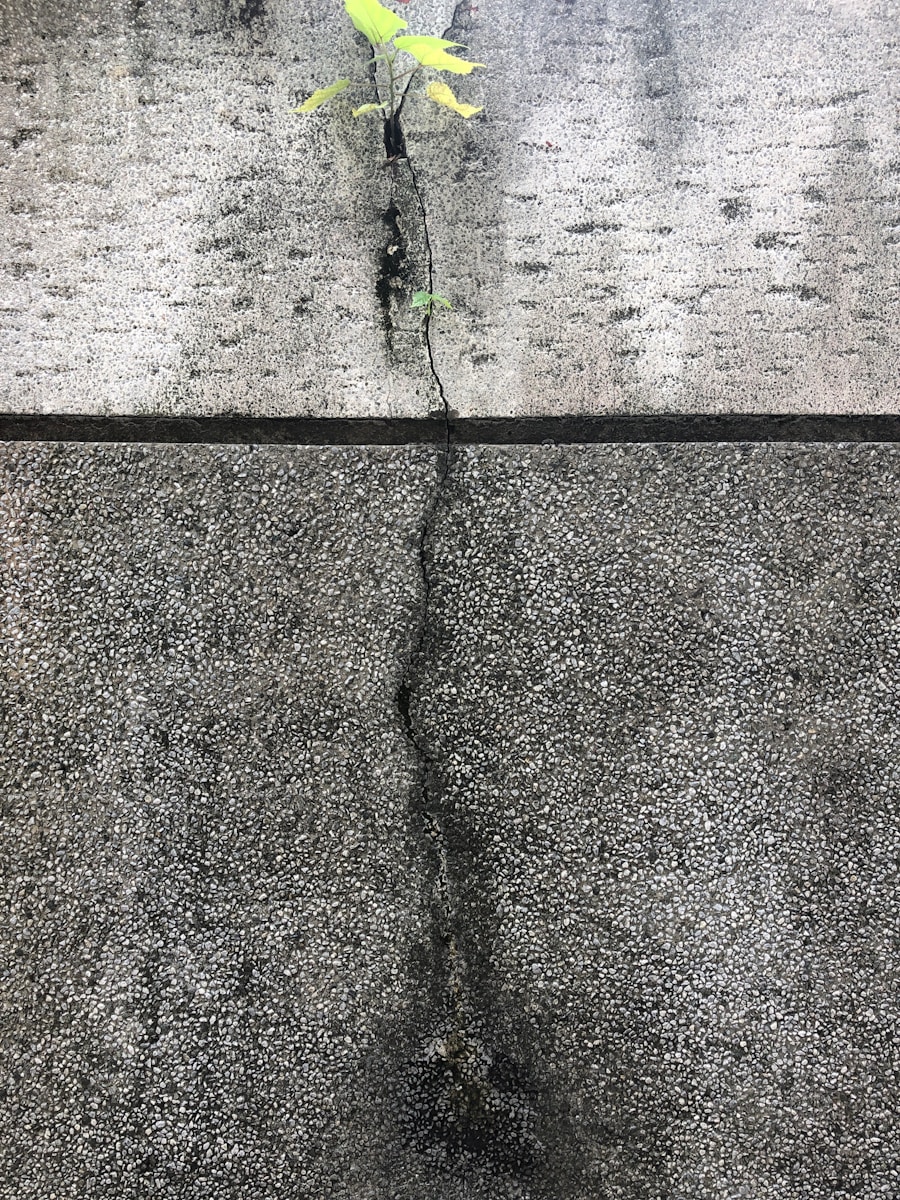

Fatigue stress and RC deterioration
By
Fatigue stress represents a critical factor in the progressive deterioration of reinforced concrete (RC) structures, particularly under conditions involving repeated loading and corrosive environments. The synergistic interaction between fatigue and corrosion, commonly referred to as corrosion-fatigue, significantly intensifies the degradation of structural materials, thereby diminishing overall structural integrity and long-term durability. Fatigue stress originates from…
-
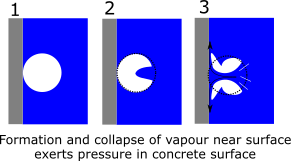
Cavitation effect in concrete
By
in EngineeringCavitation is a physical process that leads to surface pitting caused by the collapse of vapour bubbles, which results in a sudden rise in local pressure. In this article, we explore how this phenomenon can damage concrete. Damages by cavitation Cavitation can damage the concrete in the following ways: Shock Waves Generated by Bubble Implosion:…
-
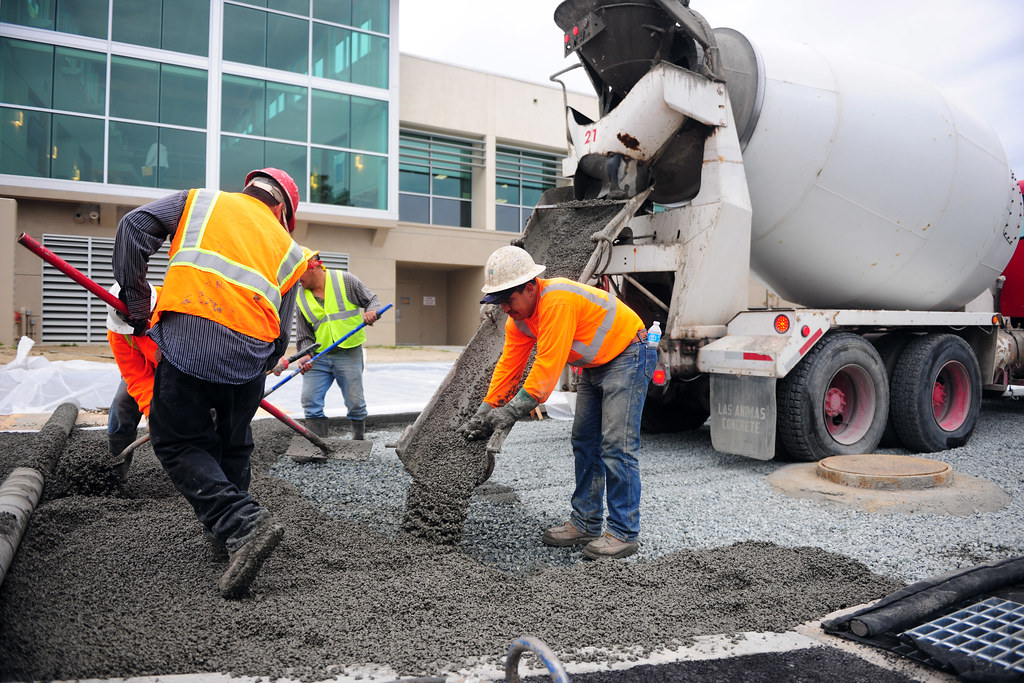

Durability of concrete in terms of water permeability
By
Permeability is one of the main indicator defining the durability of the concrete. In one hand, the permeability of the concrete can be high from the beginning of concrete life, in which case, the deterioration takes place rapidly during the service life. While in the other hand, the permeability of the concrete may gradually increase…
-
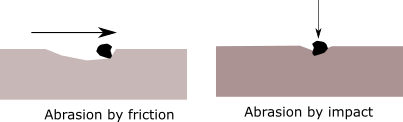
Degradation of concrete by abrasion
By
in EngineeringAbrasion of concrete is progressive loss of concrete mass due to mechanical degradation such as friction, grinding action, impact, overloading and local crushing. Vehicular movement and pedestrian traffic causes abrasion. The worst effect of abrasion is caused by vehicle with studded/chain tyres. Similarly, in industrial buildings, the concrete floors are subjected to impact load and…