How to
-

Radius of earth (classical trigonometry)
By
Suppose that, while lying on a beach near the equator watching the sun set over a calm ocean, you start a stopwatch just as the top of the sun disappears. You then stand, elevating your eyes by a height H=1.7m, and stop the watch when the top of the sun again disappears. If the elapsed…
-

Gödel Number encoding from mathematics into arithmetic
By
Kurt Gödel’s Incompleteness Theorems revolutionized mathematical logic by demonstrating the inherent limitations of formal systems. A crucial component of his proof was the technique known as Gödel numbering, which allows mathematical statements, proofs, and logical operations to be encoded as numbers. This technique transformed logic into arithmetic, enabling self-referential statements that underpinned his groundbreaking theorems.…
-

A note in abacus
By
There are several types of abacuses (or abaci) used throughout history and across different cultures. The most popular ones are from China, but there are other abacus that were developed independently. This article gives glimpse of some of the popular abacus. Types of abacus 1. Chinese Abacus (Suanpan) The Suanpan typically has 2 beads on…
-
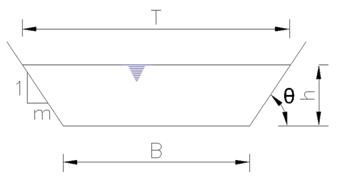
Most efficient trapezoidal section for flow propagation
By
Calculating the most efficient trapezoidal section of a canal is crucial for optimizing water flow and minimizing the construction cost. A trapezoidal canal section, characterized by its trapezoidal shape, allows for controlled flow and effective sediment transport. The most efficient trapezoidal section of canal can be calculated as follows Let, Base width of the canal=B…
-
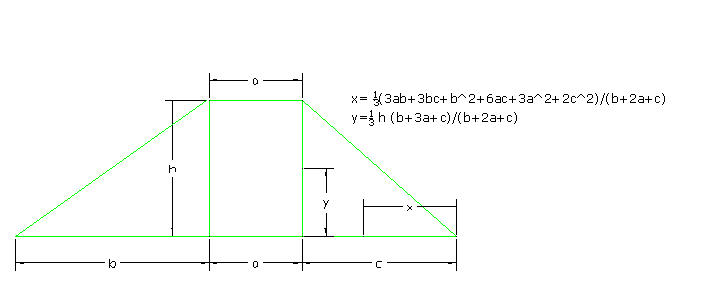
Centroid of trapezoidal shape
By
in How toThe centroid of the trapezoidal with its one face perpendicular is given be $$ X=-1/3* {(-2b^2-2*a*b+a^2)/(a+b)}$$ $$Y=1/3 *h* (b+2*a)/(a+b)$$ Where a, b, h and origin is as shown in the figure below. Similarly, the centroid of any trapezoidal that does not have perpendicular face is given by $$x= 1/3*(3a*b+3*b*c+b^2+6*a*c+3*a^2+2*c^2)/(b+2a+c)$$ $$y=1/3* h* (b+3*a+c)/(b+2*a+c)$$ Where a, b…
-
Common problems in Autocad and their solution – a historical database
By
in How toI am listing a set of AutoCAD commands and system variable which just offends the regular users. Use F1 in the AutoCAD for details. Problem: Land Desktop import slope lines in plan view Solution: To import end lines (lines meeting to ground in fill or cut): Cross section->Point Output->Catch Pt to DWG-> Yes ->…
-
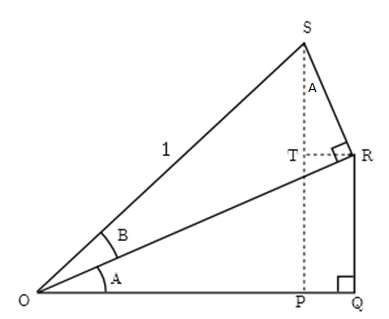
Derivation for sum of angles
By
The summation formulas for sine, cosine, and tangent are the key identities that govern trigonometric relationships. These formulas help us analyze combinations of angles in various scenarios, from simple geometric calculations to complex oscillatory systems. Let’s revise these fundamental concepts.
-

Counting the number of words in MS-Word using Fields
By
in How toCounting the number of words in MS Word document can often feel like a straightforward task—until you need to exclude certain sections like titles, references, or footnotes. Whether you’re preparing a manuscript, a report, or an academic paper, accurately tracking the word count can make a significant difference. Here’s a handy guide to help you…
-
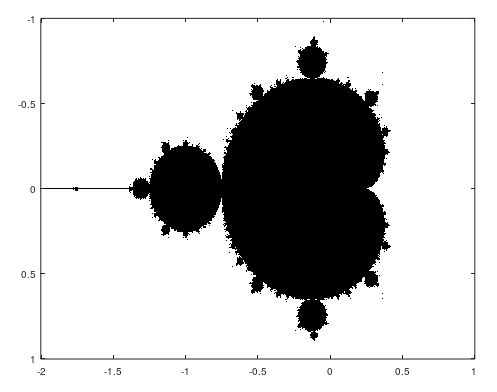
Fractals programming
By
Fractals are intricate geometric patterns that exhibit self-similarity across various scales. They are created by repeating a simple process, leading to complex structures often found in nature, such as snowflakes, coastlines, and tree branches. The concept of fractals challenges traditional notions of geometry, as they possess non-integer dimensions, meaning their detail increases infinitely with magnification.…