Engineering
-

Robotics for aging populations
By
Robotics for aging populations is an emerging field that addresses the growing need for innovative solutions to support the elderly. As the global population ages, with projections indicating a significant increase in the number of individuals aged 65 and older, robotics offers promising avenues to enhance the quality of life for older adults. These technologies…
-

Oblique wing aircraft
By
The oblique wing aircraft, also known as pivot wing or slewed wing aircraft, represents a radical departure from conventional aircraft design, offering the potential for significant improvements in aerodynamic efficiency, fuel economy, and performance across a wide range of speeds. Unlike traditional fixed-wing or swept-wing designs, the oblique wing features a single wing that pivots…
-
History of touchscreen technology
By
Touchscreen technology has revolutionized the way humans interact with machines, transitioning from traditional input devices like keyboards and mice to more intuitive and tactile interfaces. From its origins in the mid-20th century to its ubiquitous presence in smartphones, tablets, and kiosks, touchscreen technology represents a significant leap in human-computer interaction (HCI). This essay delves into…
-

Principles and application of smart materials
By
Smart materials embody a convergence of material science and technology, leading to innovations that were previously unimaginable. For instance, shape-memory alloys (SMAs) and piezoelectric materials are quintessential examples of responsive materials that can convert one form of energy into another, providing unique functionalities. SMAs, such as Nickel-Titanium (Nitinol), exhibit the extraordinary capability to revert to…
-

Refresh rates of display screens
By
The refresh rate of a display, measured in hertz (Hz), refers to the number of times the screen refreshes its image per second. For instance, a display with a 60 Hz refresh rate updates the screen 60 times every second. While this may seem like a minor technical detail, the refresh rate plays a crucial…
-

Advancement in human augmentation
By
Human augmentation represents a significant leap forward in the convergence of biotechnology, cybernetics, and artificial intelligence, among other fields. The goal is to enhance human physical and cognitive abilities far beyond their natural limits. This convergence has already started to blur the boundaries between human and machine, creating profound implications that warrant thorough investigation. Biotechnology…
-
Early days of FEA
By
in EngineeringDuring the 1940s, the world was embroiled in World War II, and the demands for more advanced and efficient aircraft surged. Aircraft engineering faced challenges due to the increasing complexity of designs, as manufacturers aimed to build planes that were lighter, faster, and more durable. This pressure led to the development and early application of…
-
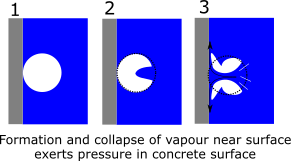
Cavitation effect in concrete
By
in EngineeringCavitation is a physical process that leads to surface pitting caused by the collapse of vapour bubbles, which results in a sudden rise in local pressure. In this article, we explore how this phenomenon can damage concrete. Damages by cavitation Cavitation can damage the concrete in the following ways: Shock Waves Generated by Bubble Implosion:…
-

Science of engineering tapes
By
When one thinks about tapes, one might imagine a simple roll of something sticky. But dive into the aisles of a hardware store, and you’ll find a world of tapes with unique powers—some strong enough to fix a broken car bumper, others designed to hold up in the rain, and some even with colours and…
-
Impact of finite element analysis
By
in EngineeringFinite Element Analysis (FEA) has become a cornerstone in modern engineering, evolving from its humble origins into an advanced computational technique that touches virtually every aspect of structural, mechanical, and material engineering. Its development traces back to the mid-20th century, born out of the need for more accurate solutions to complex engineering problems that could…